www.sciencedaily.com
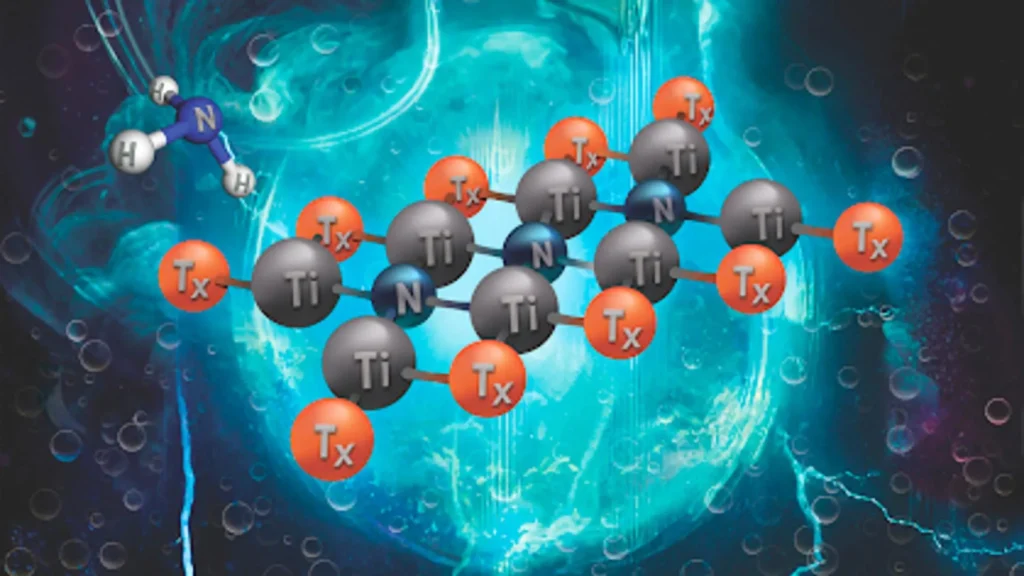
MXenes, a class of two-dimensional materials, are emerging as potential catalysts for converting atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia. This process, vital for producing fertilizers and clean fuels, could be revolutionized by MXenes’ tunable atomic structures. Researchers are focusing on customizing MXene compositions to achieve optimal catalytic performance, presenting a more efficient and cost-effective alternative to traditional, expensive catalysts currently used in ammonia synthesis. This research aims to develop cleaner and more sustainable methods for producing essential resources.